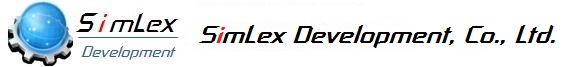Master Production Schedule(MPS) and Material Requirements Plan(MRP)

Positioning of MPS and MRP
What is MPS
What is MPS (Master Production Schedule)?
The target of the MPS is finished goods. MPS serves as a cushion between the order information, unofficial orders, forecasting, and the manufacturing plan.
In other words, if production is carried out in accordance with the order information, unofficial orders, and forecast, the manufacturing load will be unstable and stable production will not be possible. MPS is created to alleviate this manufacturing load spike.
Here, when creating a standard schedule production plan, it is necessary to
(1) Create an appropriate lot structure that facilitates manufacturing.
(2) Level the load balance. (Quantity leveling, production ahead of schedule, etc.)
(3) Consider safety stock against fluctuation of unofficial information and forecast.
(4) Create a planned inventory MTS (Make To Stock)
Mater Prduction Schedule MPS Methodology
(1) Appropriate lot configuration for ease of production is performed.
The reasons for the need for an appropriate lot structure are as follows
・Large manufacturing lots cannot be produced in advance. Large lots require lot-splitting.
・If the lot size is too large, production progress and inventory will be reflected too slowly when improving production results. Experience shows that lot size should be 1/3 or less of the daily production volume.
(2) Level the load balance. (Quantity leveling, production ahead of schedule, etc.)
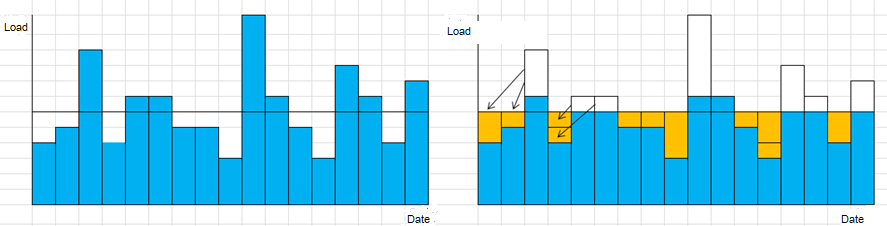
Loads are generally managed by number of pieces. Time management is difficult.
In kanban production, the standard schedule production plan is also created and the daily parcel allocation process is exactly what is used to equalize the number of pieces.
The daily parcel allocation process is exactly what is needed to equalize the number of pieces.
(3) Considering safety stock in response to fluctuations in informal orders and forecasting.
The fluctuation of informal offers from customers is about 10-15% in the automotive industry.
Forecasts are generally prepared by the company’s own sales staff. For their own safety, sales staff often make a larger inventory than actual.
Safety stock must be constantly maintained according to the amount of demand.
(4) Make To Stock (MTS) of planned inventory
MTS is a traditional production strategy, especially effective for prospective production type companies.
The effectiveness of planned inventory MTS depends entirely on correctly forecasting demand.
What is MRP
What is Material Requirement Planning (MRP)?
Material Requirement Planning is to calculate the net requirements of purchased and manufactured goods based on the production plan of the base schedule.
In simple terms, MRP calculates the quantity of work in process, the quantity of finished goods to be produced, and the quantity of purchased goods to be ordered, based on the effective inventory allowance from the quantity of goods to be shipped in the future.
Gross Requirements = Gross Demand
Net Requirements = Total Requirements – Effective Inventory
Effective Inventory of Purchased Goods = Current Inventory + Ordered Quantity – Planned Consumption Quantity – Safety Stock
Work in Process = Current Inventory + Planned Production Quantity – Planned Consumption Quantity – Safety Stock
Finished Goods Availability = Current Inventory + Planned Production Quantity – Planned Shipment Quantity – Safety Stock
SimLex Material Requirements Planning MRP Features
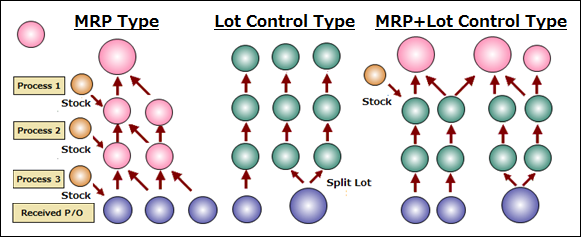
Calculate requirements for the two types of management as described above. (Mixed use is possible.) ・Lot Control Type is a production method tied to an order.
Lot Control Type (Lot Control Type) is a method in which production is linked to orders and each process produces the same lot size without inventory allocation.
In MRP Type, all processes are allocated inventory and each process produces in a size that is easy to produce.
Parameter settings for SimLex requirements calculation
| Parameter name | Contents |
| Calculation period of MRP | The start date can be the same day for up to one year. No setup required, automatic |
| Official and Unofficial periods | Setup of Official and Unofficial periods for each item of FG, subcontracted goods, and RM, and creation of Official and Unofficial periods. |
| Lead time | Configurable manufacturing lead time, transport lead time (supported by scheduler only), receiving lead time, ordering lead time, etc. |
| Order Policy | Selects one of the following options: “Lot,” “Day,” or “Lot + Day”. |
| lot size | Sets order lot size (SOQ), minimum lot size (MOQ), and economic lot size (EOQ) |
| Summary days | Sets the number of summary days |
| Safety stock | Sets safety stock per item |
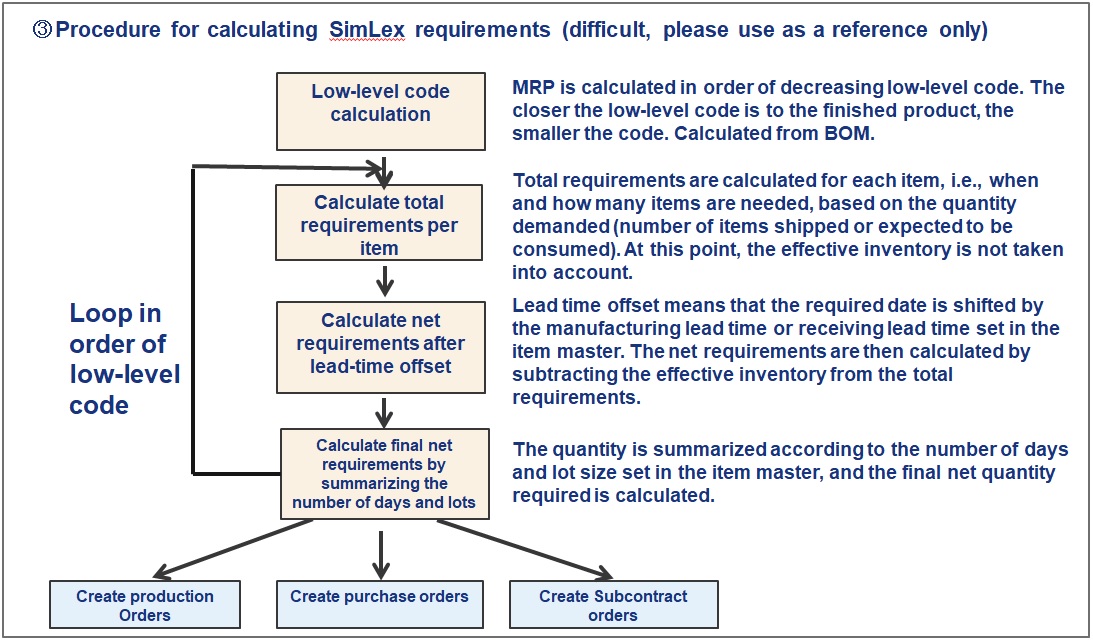
③Procedure for calculating SimLex requirements (difficult, please use as a reference only)
④SimLex MRP Simulation Capabilities
The MRP simulation can simulate MRP based on both the standard schedule production plan and new customer orders that have not yet been registered in the standard schedule production plan.
MRP simulation is based on the base schedule production plan and new customer orders that have not yet been registered in the base schedule production plan.
SimLex Developmet Co., Ltd. Toshio Koga

After graduating from Kyushu University, he worked for a major bearing company and experienced process design in the production technology laboratory. After that, he established SimLex Development Co., Ltd. in Thailand, where he has been developing and selling ERP, production management systems, and accounting systems from zero-based systems up to the present.